The drying process of heat shrink film adhesive refers to the process of evaporating the solvent or water in the adhesive layer applied on the substrate, thereby curing the adhesive. Due to the time required for solvent or water to evaporate, drying is a relatively slow step in the production process of protective films. The drying speed not only determines the production speed but also greatly affects the quality of the product.
In actual production, various manufacturers control the heat sealing strength as an important quality indicator for both bag making products and coil products used in automatic packaging production lines. Based on practical production experience, a brief analysis will be conducted on the factors that affect the heat sealing strength of heat shrink films:
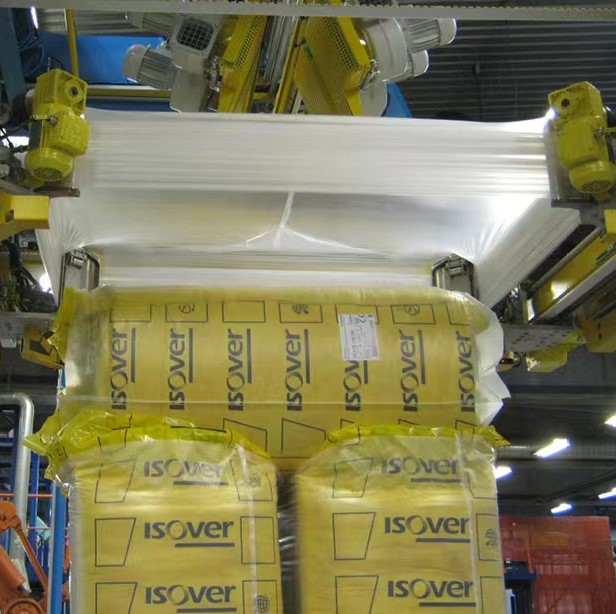
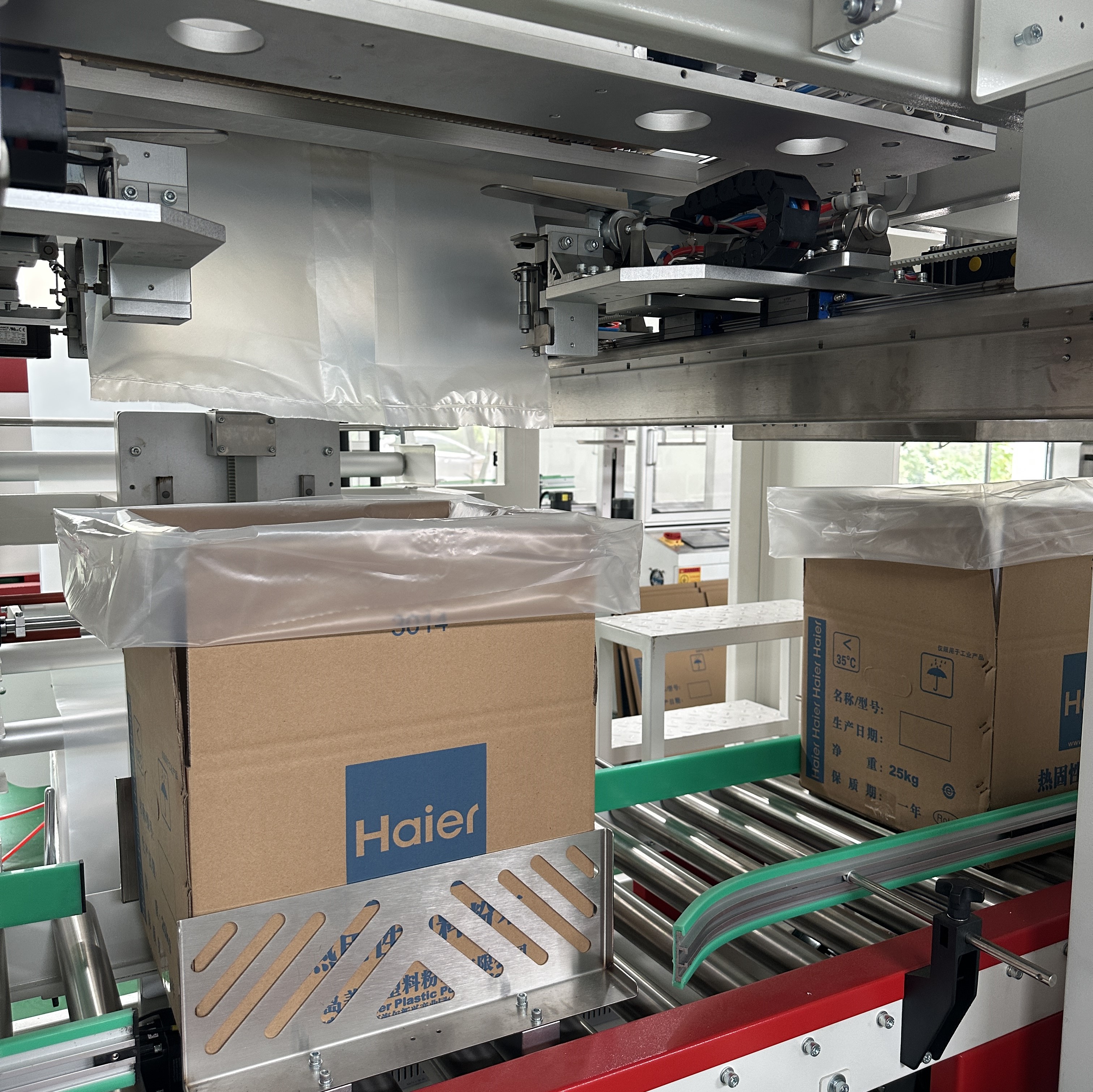
1、 Heat sealing time: The heat sealing time of automatic packaging machines or old-fashioned bag making machines is determined by the machine speed. The longer the heat sealing time, the stronger the bonding between the heat sealing layers, while keeping the heat sealing temperature and pressure constant. But if the heat sealing time is too long, the heat sealing part of the composite film will have wrinkles and unevenness, seriously affecting the appearance quality of the product.
2、 Heat sealing pressure: In order to ensure the heat sealing strength of plastic composite flexible packaging, a certain heat sealing pressure is essential. Therefore, during the heat sealing process, it is required that the heat sealing pressure is moderate and uniform. If the heat sealing pressure is insufficient or uneven, it will cause bubbles to form in the heat sealing area, resulting in poor heat sealing.
3、 Heat sealing temperature: The heat sealing temperature directly affects the heat sealing strength of plastic composite packaging products.
Once the adhesive for heat shrink film is applied, the solvent will quickly evaporate before it enters the drying oven of the dryer. However, due to the heat absorption caused by volatilization, the surface temperature of the adhesive layer decreases, resulting in a decrease in volatilization rate. When the protective film enters the oven, the heat absorbed by solvent volatilization is supplemented by the heat transmitted from the outside. When the heat reaches equilibrium, the surface temperature of the adhesive layer and the volatilization rate of the solvent can also remain constant.
The viscosity and other rheological properties of heat shrink film adhesives are also factors that affect the coating process of protective films. The greater the deviation of the rheological properties of the adhesive from Newtonian fluid, the more likely it is to encounter various quality problems during the coating operation, especially when the adhesive exhibits the properties of an expanding body. Due to the rapid increase in viscosity with the increase of coating speed during the coating process, a large mechanical force must be used to unfold the adhesive. Therefore, the faster the coating speed, the less likely it is to obtain a uniform coating.

 4000538828
4000538828